The tips tips.wapka.site
T I P S
Why Is The Sahara Desert Expanding (7)
What Is The Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert spans approximately 9.2 million square kilometers and is in fact the largest hot desert in the world. Located in North Africa, it covers parts of eleven countries, including Chad, Egypt, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Western Sahara, Sudan, Algeria, and Tunisia. This expanse of arid land is characterized by its often harsh climate, with massive temperature swings that can soar above 50 degrees Celsius during the day and plummet below freezing at night.
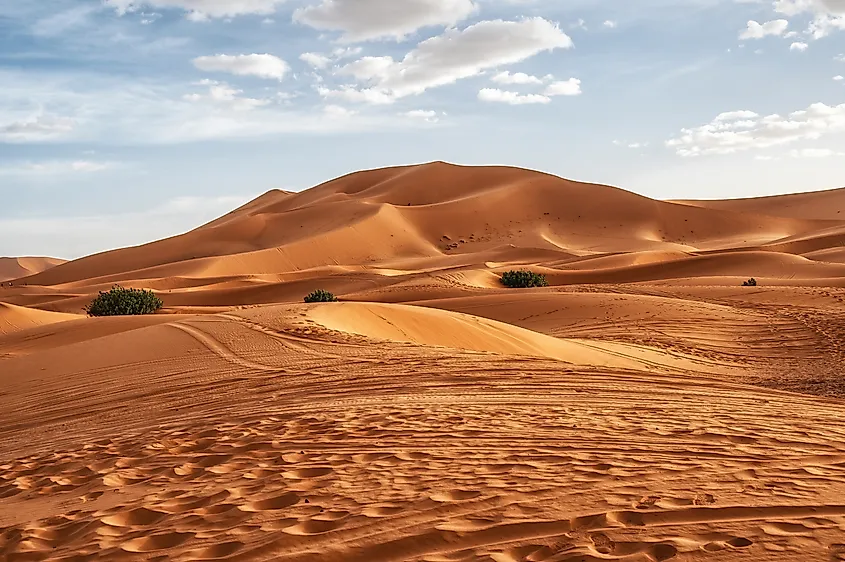
The Sahara's Geographic Landscapes
The Sahara is built up of a diverse amount of geographic landscapes, comprising mainly of sand dunes, gravel plains, rocky plateaus, and even some mountain ranges, such as the Ahaggar (with peaks rising above 9,500 feet) and Tibesti ranges (containing Mount Emi Koussi, a peak that rises a lofty 11,204 feet). Its iconic sand dunes, particularly in Algeria and Libya, can reach heights of up to 180 meters!
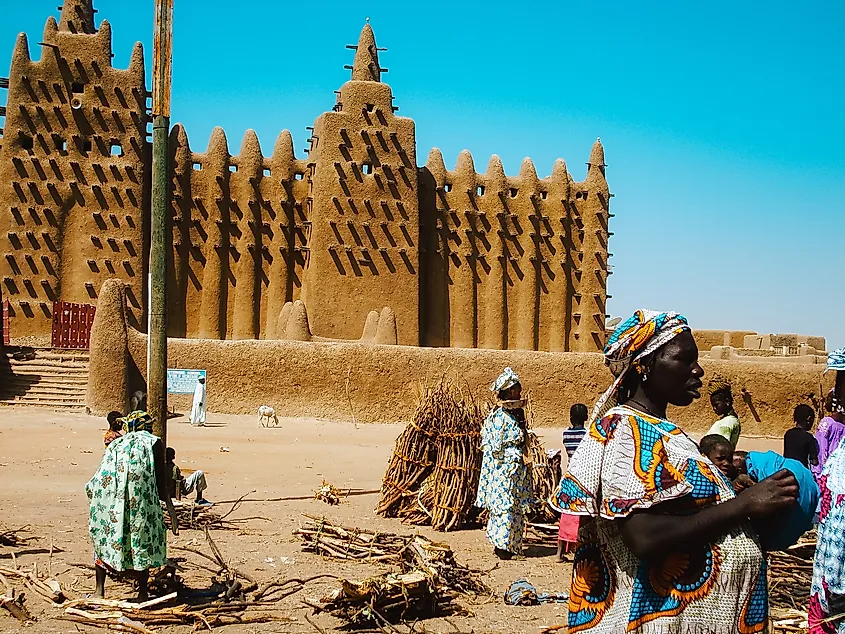
Human Settlement And Historical Significance
Human settlement in the Sahara Desert is limited but historically significant. Nomadic tribes, such as the Tuareg and Berbers, have traveled this desert for centuries, passing through it mainly for trade while other groups of people wouldn't dare try (understandably). There are some oases, providing vital water sources, that serve as hubs for small to medium-sized towns and cities, like Ghardaia in Algeria and Timbuktu in Mali, the latter being a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Is The Sahara Growing
The short answer is yes. But, how do we know this? A number of studies, including one that spanned 93 years by researchers at the University of Maryland, have concluded that the sands of the Sahara have been expanding for some time, primarily southward into the Sahel region. Having grown an estimated 10% since 1920, this is an undeniable fact that continues to be demonstrated year after year, with expansion often at its fastest during the summer months when the already dry desert becomes even more absent of water.
What Could Be Causing It To Grow
The growth of the Sahara Desert is mainly driven by natural climate variability and human-induced climate change. Naturally, a process called the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), a periodic climate cycle in the North Atlantic Ocean, significantly influences this expansion by affecting regional rainfall patterns. In the case of the Sahara, during warm phases of the AMO, this region experiences drier conditions, causing the desert landscape to spread.
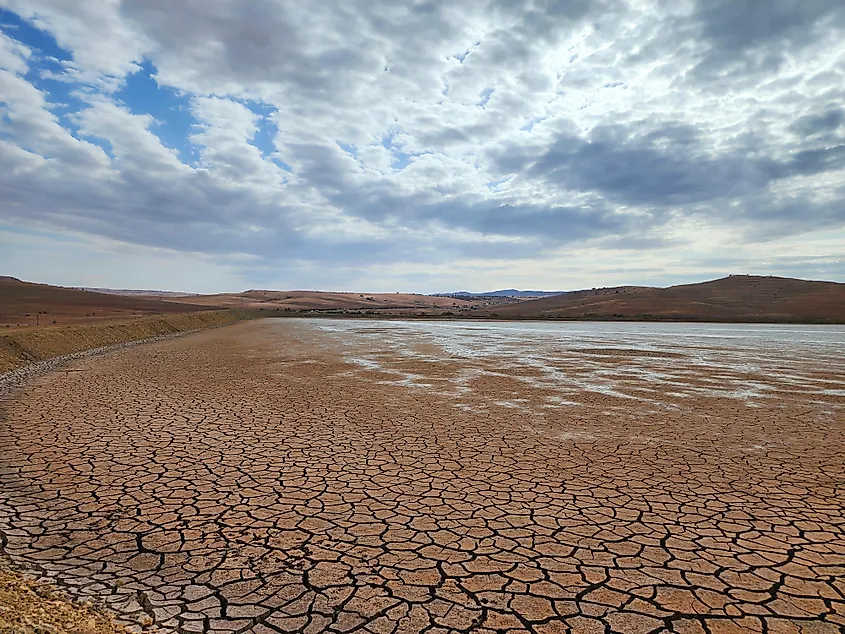
Greater Issues Related To This Changing Landscape
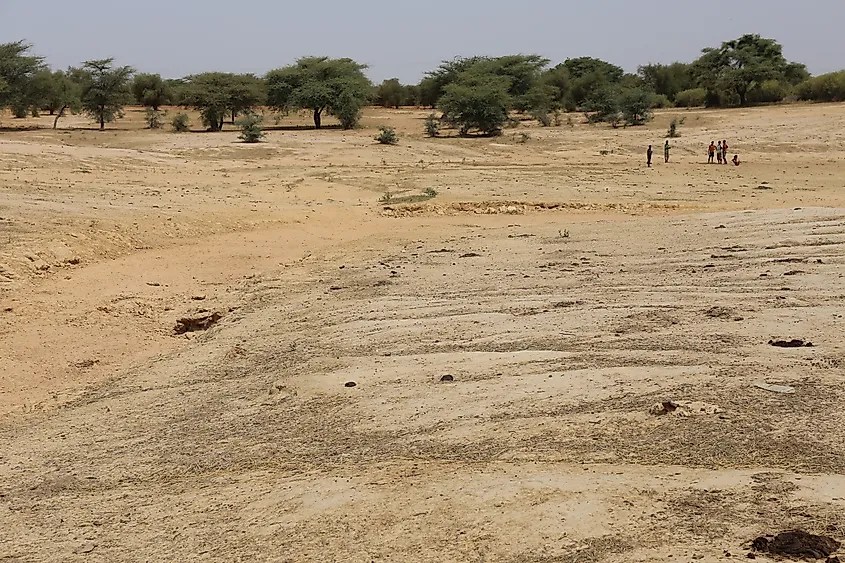
The Sahara Desert's expansion is causing significant environmental and socio-economic issues. As mentioned, the southward creep of the desert into the Sahel is exacerbating drought conditions, making it difficult for local populations to maintain their agricultural and pastoral livelihoods. The loss of this farmland leads to food insecurity, pushing communities into poverty and increasing competition for resources. This can, and sometimes has, resulted in conflict and displacement as people migrate in search of more habitable areas.
Strategies To Combat Desertification In The Sahara
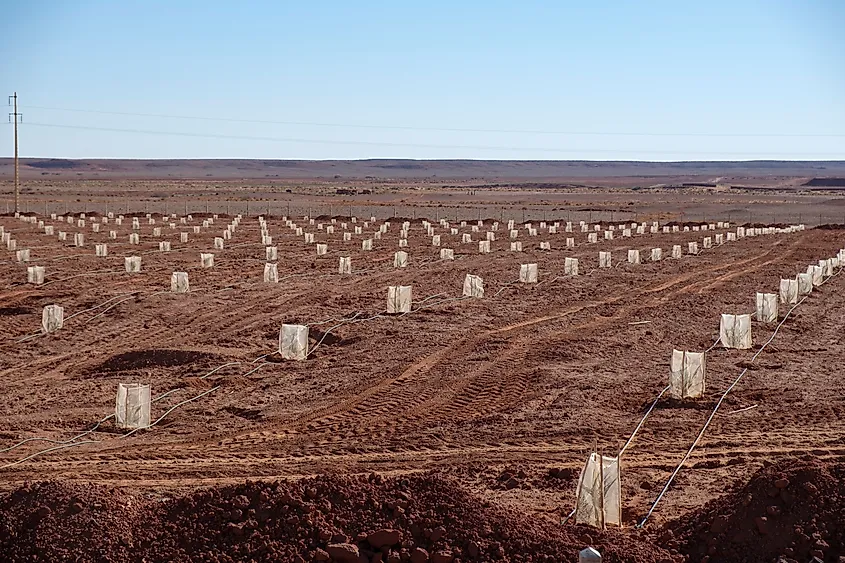
As mentioned before, the Sahara's growth results from the complex interplay between natural cycles and climate change. Tackling this issue requires understanding these drivers and implementing strategies to mitigate their impacts on vulnerable regions. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting sustainable land management practices are some of the steps we can also take part in to help address the root causes of desertification.
Total (1)
Why Is The Sahara Desert Expanding (7)
Total (0)
Tips